- Introduction
- CFD Underlying Assets
- What Assets do CFD Finance Cover?
- A Look at Financing a CFD Trade
- CFD Trading Finance Risks
- How do You Finance or Place a CFD Trade?
- How much can You Trade?
- The Bottom Line
Introduction
Contract for Difference or CFD represents the difference between the price when you buy and sell a CFD of an index, commodity or a share. CFD represent the contract between a buyer and a seller. The investor and broker agree to exchange the difference between the price of a share at the opening and closing of a trade. The management of cash and other assets in CFD trading could be referred to as CFD finance.
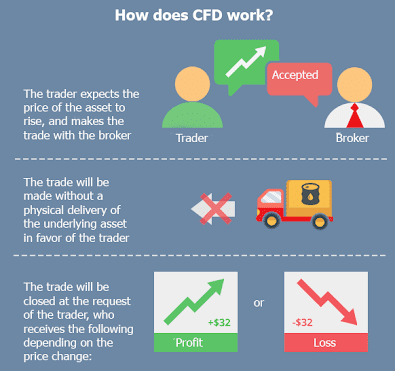
All CFD trading is financed in cash. The success of your trading is proportional to the amount of cash that flows into or out of your account. Understanding CFD finance; how money, commission, fees and other assets are used in CFD trading will contribute to your success. As a known financial tool CFD allows investors to purchase or sell at a certain price a contracted number of shares in a given stock. You don’t have any additional benefit of owning a share because you don’t own the underlying assets.
CFD Underlying Assets
The CFD underlying asset is the price of a CFD derived from a physical asset in the market. This could be a share in the stock market, commodity, index or foreign exchange markets. The price of the underlying asset is the same with the price of the CFD. Majority of CFD brokers offer a large range of underlying markets. CFD traders bet on the future price of these underlying assets but they don’t own them.
What is Product Disclosure Statement?
CFD provider typically provides a document to the trade called product disclosure statement. Product Disclosure Statement contains detailed information on finance, markets and trading examples also highlighting the risk of CFDs. The product disclosure statement may appear discouraging because of it’s lengthiness but it contains vital information. Take time to study it before you open an account.
What Assets do CFD Finance Cover?
You can trade CFDs on a wide range of different financial assets. This depends on the access that your CFD provider has to various underlying asset price feeds. However the range of markets available to trade is on constant increase. The main CFD market types include but not limited to the following:
Global stock CFDs, examples: Australia, United State, United Kingdom, Asian and European
Stock index CFDs, examples: Tesla, Dow, Apple, NIKKEI, etc
Forex CFDs
Industry sector CFDs, examples. IT, manufacturing, media, oil and gas, banks, technology, etc.
Commodity CFDs, examples: soft commodities and grains.
Metals and energy CFDs, examples: diamond, copper, gold, silver, oil, natural gas, uranium, etc.

Sector CFDs
One of benefits of CFD trading is that it allows you to profit anywhere in the world where you find a growth opportunity. Traders could well profit from a declining economic sector, as it is easy to go short or long.
For instance, view the economy exhaustively with sector CFDs and choose for example IT as a solid growth industry. This saves you from analyzing the individual companies because you only need to focus on the big economic picture to select profitable areas to trade. You have access to diversification which reduces volatility associated with single stocks with sector CFDS.
Bear in mind of the tendency of sector CFDS to have bigger spread compared to CFDs on individual stocks. A given sector that is dominated by one or two large firms, it may be cheaper for you to trade CFDs on the individual companies instead of taking up the sector CFD.
Share CFDs
In the marketplace, the most commonly traded CFDs are the shared CFDs. The price of the CFD in this type of contract comes from the price of the underlying stock that is the subject of the CFD. If you are experienced in trading stocks, trading share CFDs will feel exactly the same. But, be aware of some differences between the two.
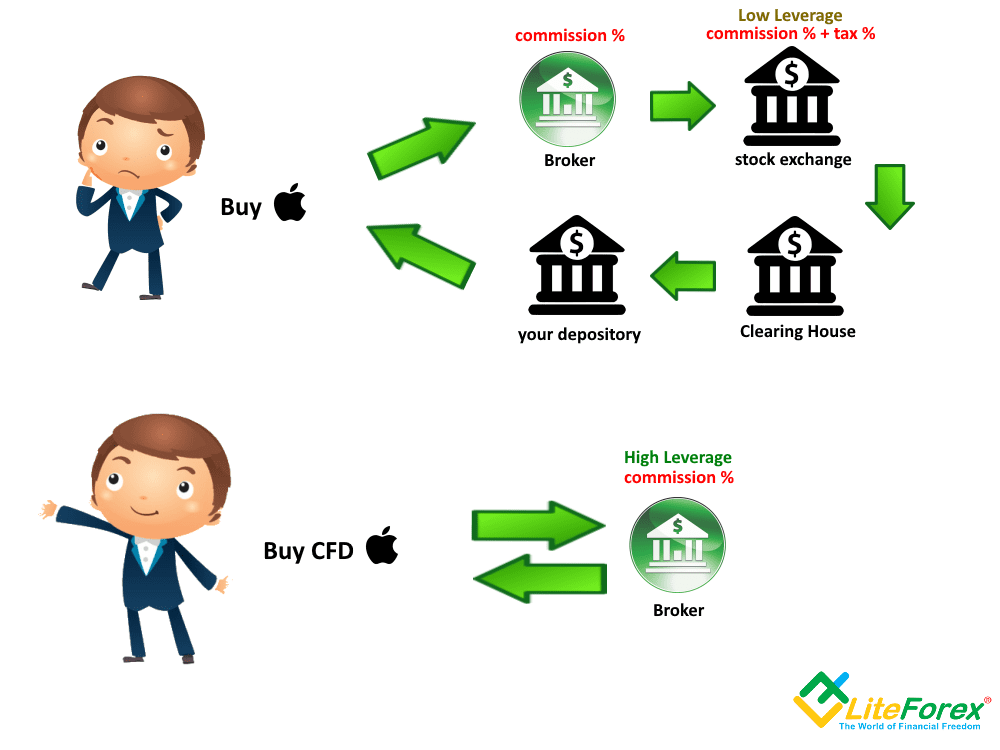
Commodity CFDs
Commodity CFDs are CFDs with commodities as the underlying asset. Commodities are in demand tangible assets. Commodities are divided into two groups: hard commodities and soft commodities. Hard commodities are mined, extracted and soft are grown. These assets are usually similar in quality from one item to the next and is known as a fungible good. For instance, one cocoa is the probably the same as the next cocoa. Common commodities for CFDs include precious metals like diamond, gold etc, cocoa, corn, soya beans, wheat, natural gas, crude and heating oil. This kind of CFD gives traders the opportunity to trade the futures market with the benefits of CFD.
The CFDs advantage is they reduce the complexity associated with trading commodities on regular exchange markets like varying lot sizes and expiry dates. Moreover this CFD encourages lower trading finance, and remove the confusion of which exchanges to go to for specific commodities.
Index CFDs
Here the CFDs are tied to the performance of a specific index. Research shows that index performance contracts are attractive to CFD traders because this type of contract have high leverage possibility, liquidity, and volatility. Popular indices are the Australian Stock Exchange, Nikkei, Dow Jones, NASDAQ, and London Stock Exchange. The advantages of this kind of CFD are high leverage and trading volume, low margin and trading costs, and the access to international markets that otherwise are difficult or financially demanding. Traders of indices general belief is that a specific market will rise as a whole.
Treasury CFDs
If you favor speculating on the value of treasury notes then choose a treasury CFD. Treasury notes that are Commonly traded are US Treasury Notes of varying years, US Bonds, Euro-Bond, and Australian Treasury Bonds. There are Forex experts that offer signals on these as well.
Carbon Trading CFDs
This type of CFD market is a very recent idea, and is both volatile and political. It is a contract for difference on emission values with an underlier of the futures contract. This pollution program encourages individuals to emit a particular amount of the gas, for which they get a permit. They can sell their excess to others who need it if they improve their performance by emission reductions.
A Look at Financing a CFD Trade
Let’s say the current level of the NYSE is 4000 points. If you believe the market is going to move upwards that is trade higher, you would take a long position. In other words, you’re entering a CFD trade and thinking the NYSE 100 will move higher than it’s current level of 4000 points.
Because CFD trading are leveraged, you don’t need to outlay a large sum of finance to open a position. Instead, you place a deposit. This is called margin. Most indices are highly leveraged. Often a common place to see an index leveraged at 99:1. In this case, it means your deposit or margin is only 1% of the value of the trade to open it.
For example, if you wanted the total value of your trade (exposure) to be $40000, you would finance 10 NYSE index contracts. Therefore 10 contracts × 4000 gives you an exposure to the market of $40000. With 99:1 leverage, you would pay a margin of just $400, which is 1% of the total value of the trade. If the index rose from 4000 t0 4500 points over the next four weeks, you would have made a significant profit of $5000 ($500 CFD × 10 contracts). This a very large increase over your $400 investment. Not a bad return by anyone’s standard. But remember your losses are augmented too if you get it wrong. This means you have lost $5000. In this instance you have lost your initial investment and much more. Ensure you understand this idea very well.
CFD Trading Finance Risks
One golden rule of trading is this: Never trade with money which you cannot afford to comfortably lose. You may have heard it a thousand times but believe it. The best guard against this is a realistic view of life – not a belief that is magical or mystical force at work. This is science in addition to luck.
How Risky is CFDs?
CFD finance are incredibly risky. Its vital you understand this. The risk is not limited to your stake because your our losses could be considerably more. Let’s go back to the New York Stock Exchange index CFD trade above to show you what I mean. For instance If the index falls from 4000 points to 3700, your lose will be $3000. That is (4000 – 3700) × 10 contracts. It is important you don’t forget that, with any CFD trade you may have, you are fully responsible for the total value of the trade.
Don’t let any tiny deposit fool you. If you take out a $40000 trade size, you need to be able to back that up if the market moves in the opposite direction of your trade.
Look, that is an extreme example. In fact there is a possibility the CFD broker would have cut the trade. However they will hold you accountable for any finance (money) owing. Again this is why it not recommendable to use 99:1 leverage becomes it is very risky. Keep it small!
How do You Lose Money on CFD?
Before you open any position, ask yourself this question. Ask yourself if you can afford to lose the amount you are exposed to. If it is a no, you can not afford to lose the amount, stop right there. CFDs are different from options where you need to take out 100 contracts at a time, the minimum CFD contract is one. This gives you the ability to get a feel of trading. It is safer to start by buying or selling one contract at a time. In time, as you become more comfortable with leverage, you can buy more contracts. Sure that you understand the risks you are taking on before you get into financing a CFD trade. Take this advice: Never place trades you don’t understand.
How do You Finance or Place a CFD Trade?
First identify a CFD provider or broker you will trade on their platform. Do this after good understanding of what CFD trading is all about.
What are the Different Types of CFD Brokers?
No-Dealing-Desk broker provides direct access to the interbank market. This type of broker can either be an STP or an ECN broker (or a mix of both).
This type of broker only sends trading orders directly to market makers. They don’t bear the risks of its clients internally because they only act as an intermediary.
An ECN (Electronic Communication Network) broker only connects different market participants together via an electronic trading platform, so then they can trade with each other. While STP (Straight-Through-Processing) broker does not execute trader orders.

Dealing Desk (DD) – Market Maker
In simple term, a Dealing Desk broker is a Market Maker. They are the ones providing liquid assets for its traders by offering their own prices. The very reason they are called market makers because they are the one that create the market for their clients. DD broker regulate the bids and prices of any financial instruments offered.
Consequently, a Dealing Desk broker pays for profitable client trades with their own money. If an investor makes a successful trade, the broker loses money – and vice versa.
Placing a CFD Trade
To place a trade, just put a call across to your CFD broker or log on to their trading platform and enter the trade. After which you will receive a confirmation of your trade. As a newbie, most dealers will take time to help walk you through a trade.
Moreover, most CFD brokers have extensive online tutorials to show you how to get started with your first trade. Many CFD providers even have a client services team that will walk you through how to place your first trade over the phone. Take advantage of these avenues and information.
How much can You Trade?
How much you can trade strictly depends on the amount of money you have deposited in your CFD account. Never forget that if a bid goes against you, you must be able to pay the full value of the trade. Often times, losses will simply be deducted from the cash in your CFD account. Always make sure you have the money to cover any loss. Don’t trade money you cannot comfortably afford to lose. Ensure you have a good understanding on how leverage works before trading. The amount of trades you are permitted to place depend your financial wherewithal and the finance that are available in your account.
Do You Need Cash to Start?
The answer is a big YES. As you open an account, it is a requirement for you make a cash deposit. This deposit will serve as security against any trades that you make. It is important to bear in mind that you can lose more than the balance in your account. Moreover the CFD broker will email or call you whenever the market moves sharply against you. This call is known as margin call. You must be prepared to pay the margin call or close out your trade and take the losses.

The Bottom Line
Financially there are many advantages of in using a CFD broker and trading CFDs. CFD trading have a wide range of markets and assets you can trade on.
CFD trading allows you to place much smaller trades compared to the usual minimums allowed in trading shares and futures directly. You can deal 24 hours a day. Deals can be conducted immediately. They quote a price and if you take it, on the spot the deal is done. You do not have to wait for the deal to be executed in the underlying asset.
CFD Financing Charges
All but share CFDs there is almost no commission to pay. Most CFDs brokers make their money on the spread of their quotation. However, be aware of a charge called Financing Charge which is applicable when trading on CFDs on shares, sectors and indices but not on commodities. Financing charge is there simply because you are borrowing from your CFD broker in order to trade the performance of an actual share. You need to pay the interest to the CFD provider, just like when you borrow to buy a car or house. This interest payment is what is referred to as financing and is usually referenced to a benchmark interest rate.

Financing charges differs depending on the CFD provider. Most times however it can be about a small percentage above the relevant benchmark interest rate for that country. Your CFD provider’s product disclosure statement should contain all this information. If it is not provided by the CFD provider, get another broker. This document should be very clear and disclosed upfront. The document may be lengthy but ensure you read the CFD broker’s product disclosure statement, PDS thoroughly. And if you don’t understand any part seek further clarification from your CFD broker. This legal document contains all the information you need to know about CFDs offered by the broker.

Pingback: FxPro Minimum Deposit and Accounts: All You Should Know